MongoDB Architecture
MongoDB is a leading NoSQL, document-oriented database known for flexibility, high performance, and scalability. Unlike traditional RDBMS, it stores data as BSON (Binary JSON) documents.
Key Features
- Document-Oriented Storage: Stores data in BSON documents, not tables.
- Schema-Less: Collections can hold documents with different structures.
- Horizontal Scalability: Uses sharding to distribute data across nodes.
- High Availability: Replication ensures data redundancy.
- Aggregation Framework: Supports complex queries and analytics.
- Fast Read/Write: Optimized with indexing and in-memory caching.
Core Components
1. Drivers & Storage Engine
- Drivers: Client libraries (Java, Python, Node.js, etc.) that connect applications to MongoDB.
- Storage Engines:
- WiredTiger: Default, supports compression and concurrency.
- In-Memory: For ultra-fast access.
- MMAPv1: Deprecated, for read-heavy workloads.
2. Security
- Authentication: Verifies user credentials.
- Authorization: Role-based access control (RBAC).
- Encryption: TLS/SSL for data in transit.
- Hardening: Restricts access to trusted hosts.
3. MongoDB Server
- Central component handling data storage, retrieval, and client requests.
- Multiple
mongodinstances can form a cluster.
4. MongoDB Shell
- Command-line interface for managing and querying databases using JavaScript syntax.
Data Organization
- Databases contain multiple collections.
- Collections hold multiple documents (records), stored as BSON.
Indexing Strategies
- Single Field: Index on one field.
- Compound: Index on multiple fields (up to 31).
- Multi-Key: Indexes array values.
- Geospatial: 2d and 2dsphere indexes for location data.
- Hashed: Supports hash-based sharding.
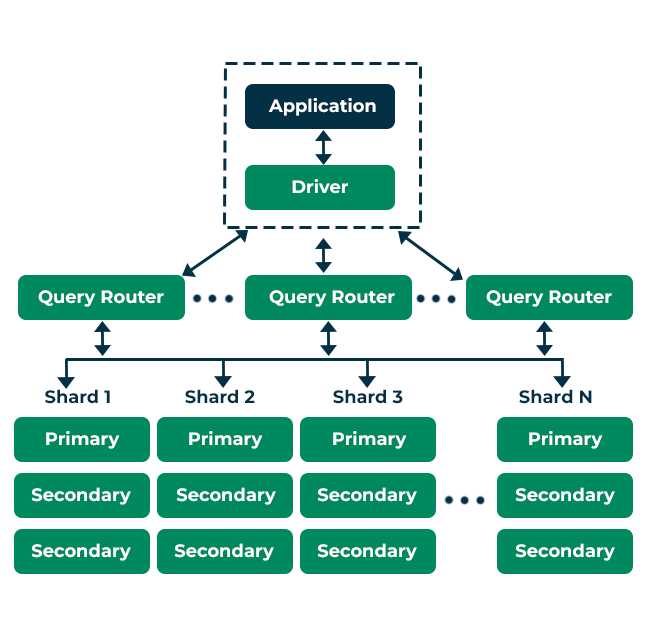
Scalability Mechanisms
Replication
- Primary Node: Handles all writes.
- Secondary Nodes: Replicate data from primary, handle reads for load balancing.
Sharding
- Distributes large datasets across multiple servers (shards) using a shard key.
- Enables horizontal scaling and fault tolerance.
Conclusion
MongoDB’s architecture—featuring document storage, flexible schema, replication, sharding, and robust indexing—makes it ideal for scalable, high-performance applications in diverse environments. Understanding these components is key to building reliable and efficient solutions with MongoDB.